FCA Wholesale Data Market Study
Read the article below or download the PDF version here.
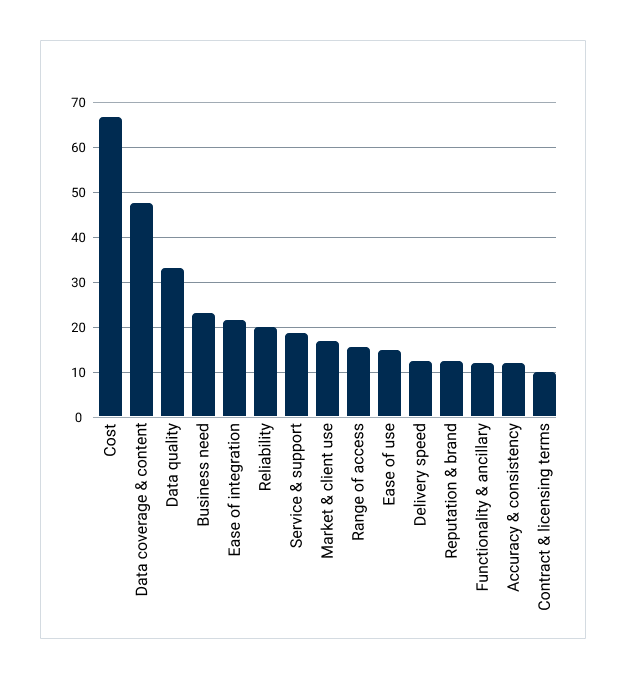
Cost, coverage and quality remain the primary concerns for wholesale market data users when selecting market data vendors.
The financial markets heavily rely on accurate and timely market data to drive investment decisions, risk management, and regulatory compliance. However, the UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has identified significant challenges in the wholesale market data industry, including high costs, limited competition, and complex licensing arrangements.
These issues lead to users potentially paying more for data and facing difficulties in switching providers due to entrenched market power and non-transparent pricing practices.
A well-functioning and accessible market for financial data is key to supporting the financial markets but data consumers continue to complain and challenge industry market data vendors on cost, coverage and the quality of the market data services they receive. Data consumers hoped to see some form of regulatory intervention into the market to address concerns around competition, cost and pricing issues subsided following the publication of the UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) Wholesale Data Market Study earlier this year.
Following a comprehensive study and review that began in March 2023 the FCA decided not to intervene in the UK Wholesale data market saying it had not found evidence that firms cannot access the wholesale data they need. The FCA did however say, that across all three markets in the scope of the study, Credit Ratings, Benchmarks and Market Data Vendors, it had identified evidence of, and drivers for, market power. This means that users may be paying higher prices for the data they buy than if competition was working more effectively.
The report outlined a number of key dynamics and challenges within the wholesale data market.
- Market concentration. A few key providers dominate and enjoy substantial market share and high profitability.
- Heavy user reliance. A significant dependency on a few data services exacerbates the lack of competition and the potential for anti-competitive practices.
- Price discrimination. Suppliers pricing data based on its perceived value to individual users rather than the actual cost of supplying it.
- Complex licensing arrangements. Licensing that did not support a transparent and well-functioning market.
- Barriers to switching. Users find it difficult to switch between suppliers due to complex contractual terms, lack of suitable alternatives and network effects, which collectively hinder competition.
- Limited Price Transparency. A lack of publicly disclosed prices making it challenging for users to compare costs with bundling practices and complex licensing terms further obscuring pricing.
Market data vendor selection
The growth in requirement for market data continues at pace, with users requiring increased frequency of data from monthly to intraday and real time. New business use cases and the increase in processing and storage capabilities within the cloud are also supporting data volume growth and the emerging demands around machine learning and AI.
This relentless growth in the need for market data combined with continuing regulatory pressures, such as MIFID and emerging ESG requirements, are putting pressure on data consumers to achieve more for their businesses while continuing to focus on managing the increasing total cost of data ownership and the market data costs.
It’s also understandable that there is frustration from users when, as the FCA reports, the Market data vendors revenues have been growing at an impressive 5% per annum in the UK since 2017 vs an inflation rate for the period calculated by the FCA to be half that at 12.9%. (2.15% avg. p.a. over 6 year period 2017-2023)
Source: UK FCA Report 29th Feb 2024
Figure. 1.0 FCA analysis of responses to our user survey
Change in total expenditure per customer
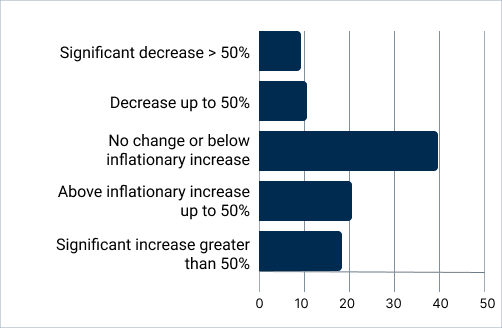
Figure. 1.1 Percentage of clients facing expenditure change of this type (%) Source: FCA analysis of MDV transaction data
The FCA survey showed:
- 24% of customers saw a decrease in expenditure between 2019-2022.
- 40% experienced an increase above inflation (12.9%), with 22% seeing an increase in expenditure over 50%
When it comes to the data quality criteria, the survey reports users' concerns around inconsistent formats, poor customer service, and lack of accountability for data errors.
- 25% of respondents feel the market delivers high-quality products at reasonable prices.
- 30% disagree, citing high prices and variable quality.
- 45% are generally positive about quality but concerned about pricing and competition.
Recommendations for improvement include better accountability, regulatory oversight, and increased competition to address user concerns and enhance market dynamics.
- Data and Service Quality: More accountability for data errors, better contracts, and SLAs.
- Regulatory Oversight: Audits on pricing models, direct supervision, and fair market behaviour.
- Usage Audits: Restrict onerous audits.
- Access Restrictions: Reduce restrictions to drive competition.
- Interoperability and Standardisation: Improve data standardisation and interoperability.
- Market Competition: Monitor M&A activities and promote low-cost providers to increase competition.
Market data vendor selection
Competition remains an issue among the Market Data Vendors with a high level of market concentration among 3 or 4 major global players leading to reduced choice, increased prices, and low incentives for quality improvement and innovation
The FCA survey relied on the responses of 7 entities, itself highlighting the limited depth of competition. The key major providers dominate market share and remain highly profitable. The concentration of global market players has been exacerbated in the past decade through significant mergers and acquisitions among data providers, benchmark providers, exchanges and credit ratings agencies including LSEG/Refinitiv, S&P/IHS Markit, ICAP/CME, ICE/IDC, Cusip Global Services/Factset.
The FCA survey respondents reported the impact of this market concentration has led to:
- Reduced choice and competition with consolidation leading to fewer options and less competition in the market.
- Increased barriers to entry make it more difficult for new entrants to join the market.
- Diminished negotiating power with users feeling they have less ability to negotiate with data providers, leading to higher costs.
- Adverse consequences: Integration of MDVs, benchmark providers, CRAs, and trading data providers has led to unfavourable commercial policies and audit practices.
- Monitoring recommendations: Users suggest that future consolidation should be closely monitored for potential negative market impacts, even for smaller acquisitions.

Challenges for New Entrants
The FCA found that 50% of users have started using a new provider in the last two years and are looking to new providers to match evolving business needs and to replace existing vendors for cost efficiency. Evolving data needs included launching new strategies, entering new markets, and sourcing specialised data like ESG or crypto. Typical barriers to entry for new firms include:
- High costs of establishing technological infrastructure and licensing data.
- Small MDVs struggle to build a large enough client base.
- Complexity of data licensing agreements.
New entrants had been seen to successfully enter the markets where they were adopting technological changes such as cloud computing, open-source software, machine learning and AI to reduce entry costs. New entrants have also succeeded in disrupting existing data business models by bypassing traditional Market Data Vendor products and asset classes.
Barriers to switching
One of the challenges to cost management and reduction regularly cited by data users are the barriers to switching vendors. Users find it difficult to switch between suppliers due to complex contractual terms, lack of suitable alternatives, and network effects, which collectively hinder competition. Some reported finding switching straightforward, while others faced significant time and resource challenges.

The main motivations for switching are:
- Cost reduction and concerns about current provider quality.
- New providers offering better data, functionality, or service
The FCA survey found:
- Around 45% of users have not switched due to meeting business needs and high switching costs.
- 20% considered switching but did not proceed.
- 40% switched or partially switched for cost reduction or better quality.
User reported barriers to switching providers included:
- High costs of switching including training, system integration, and procurement costs with user needing to coordinate complex switches across different departments to avoid data discrepancies.
- User preferences, familiarity, resistance to change and client requirements preventing migration and switching.
- Dependence on unique or proprietary data from existing providers.
- Technical and operational challenges of integrating new data sources including need to purge old data and integrate new data into systems. Contractual obligations and termination clauses.
Multi-sourcing practices
The survey found that it is common practice for users to multisource from market data vendors with only 20% of users stating they use a single market data vendor. Multi-sourcing disperses activity, reducing the strength of network effects and other benefits of multi sourcing include:
- Aggregation and creation of composite data values.
- Enhanced data consistency and verification.
- Meeting specific team or department needs with specialised tools and functionalities.
- Ensuring business continuity and resilience.
Negotiating power of users is impacted by having less competition with users ability to negotiate varying with provider size, market competition, and product criticality. Users state that smaller and new entrants to the market are often more open to negotiation to try and gain market share.
Some of the negotiation strategies applied by users include:
- Achieving cost reductions through consolidation, longer contracts, and incremental service implementations.
- Functional adjustments and reduced licenses can also be negotiated.
- Difficulty in benchmarking due to lack of published rate cards.
Users are also looking to multisource market data providers to ensure there is a level of operational resilience and to avoid dependencies on a single source.
- About 60% of users see credible alternatives for data distribution and delivery, though specialty areas may vary.
- 40% see no alternatives due to unique provider offerings or specific requirements.
Conclusion
Driving Towards a Competitive and Transparent Market
User feedback and insight from the FCA study have highlighted the need from a user perspective for several key improvements around standardising licensing and simplification of pricing, increased transparency, flexible pricing models, providing fair access to data and encouraging innovation.
The FCA's market study emphasises the critical need to foster a more competitive environment in the wholesale data market. It’s clear from the study that although there are imbalances in the data market, the approach will need to involve enhancing transparency, fairness, and reasonableness, rather than direct price regulation or product unbundling.
The FCA’s approach lays the groundwork for future regulatory actions and reforms aimed at improving market outcomes that include:
- Regulatory Framework Review: The FCA will address the study's identified issues through broader regulatory framework reviews, such as the Wholesale Markets Review and Primary Markets Effectiveness reforms.
- Consolidated Tape Development: Plans are underway to develop a consolidated tape for bonds by 2025, informed by findings from this study.
- Reasonable Commercial Basis (RCB) Framework Revisions: Potential changes to the RCB framework may be proposed to address its current shortcomings
- Ongoing Monitoring: The FCA will keep reviewing competition issues, including potential anti-competitive conduct and the necessity for action under the Competition Act 1998.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Stakeholders are encouraged to share their views on the market study conclusions.
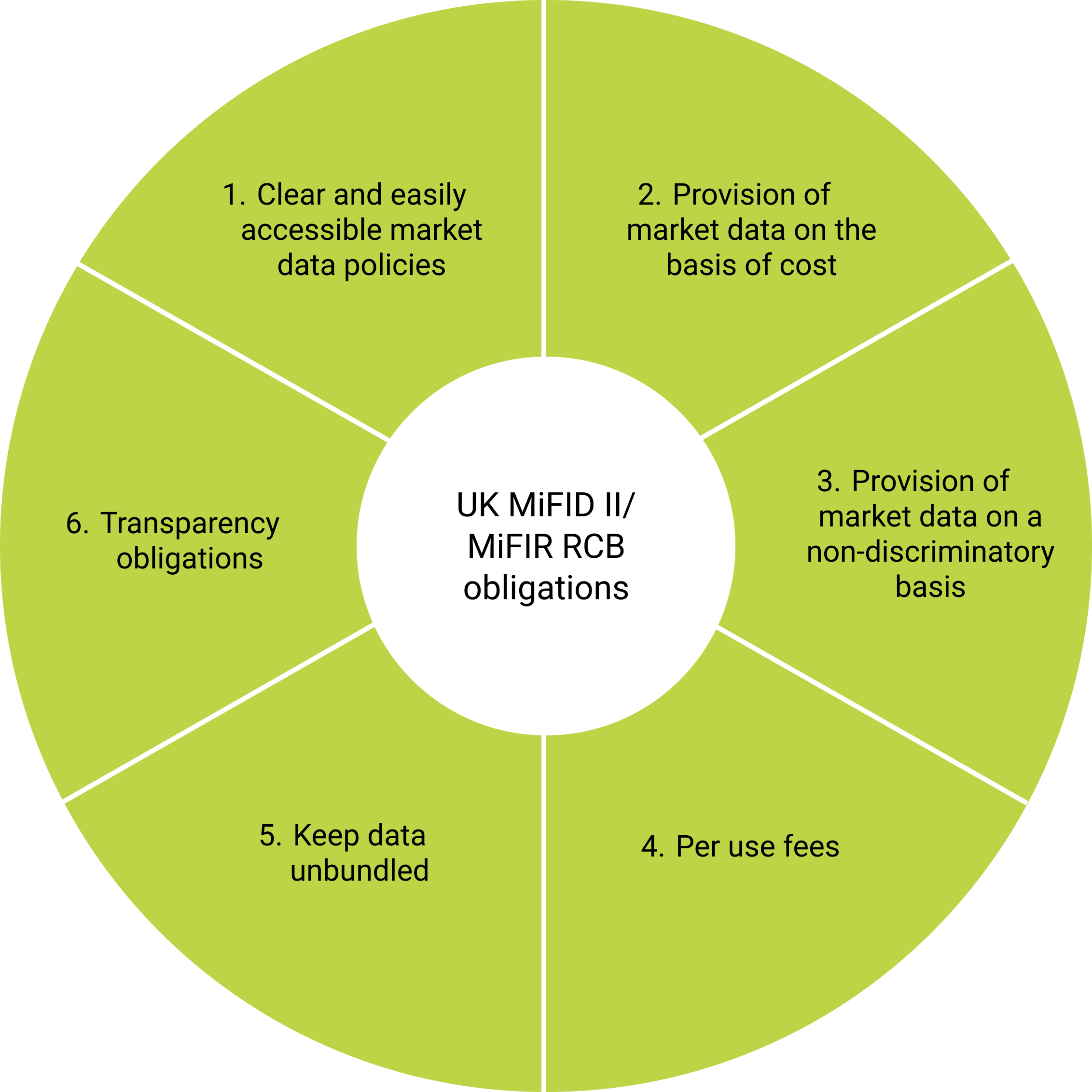
Annex 4: Market data vendors
Source: UK FCA Report 29th Feb 2024
RoZetta Technology’s DataHex platform, a cloud-based product offering, is designed to help data users improve data standardisation and interoperability, manage the total cost of data ownership, and facilitate easier switching between data vendors.
The innovative solution leverages a cloud native approach to provide a transparent, flexible, and competitive data market environment. By focusing on these key areas DataHex empowers financial institutions to optimise their data usage, reduce costs, and enhance their operational efficiency in an increasingly data-driven world.
About RoZetta Technology
A cloud-based product offering is designed to help data users improve data standardisation and interoperability, manage the total cost of data ownership, and facilitate easier switching between data vendors.
The innovative solution leverages a cloud native approach to provide a transparent, flexible, and competitive data market environment. By focusing on these key areas DataHex empowers financial institutions to optimise their data usage, reduce costs, and enhance their operational efficiency in an increasingly data-driven world.Contact Us
To learn more about how DataHex SaaS can unlock your potential for seamless collaboration and drive innovation, visit us at rozettatechnology.com or email us at enquiries@rozettatechnology.com

Peter Jones
Chief Product Officer, RoZetta Technology
Email: peter.jones@rozettatechnology.com
LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/peterdysonjones/